What Does a CDN Do?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a strategically positioned network of servers designed to deliver digital content efficiently. It facilitates the rapid transfer of essential files like HTML, JavaScript, CSS, images, and videos.
Example of How a CDN Works

Imagine a website hosted in Chicago that gets a request from a user in Washington, D.C. A CDN server nearby will deliver the content, minimizing latency and accelerating the website's loading time.
CDN vs CMS: What's the Difference?
While a CDN optimizes the speed of content delivery through techniques like caching, a Content Management System (CMS) is for creating and managing digital content. They can complement each other but serve distinct functions.
CDN and Web Servers: How They Differ
Unlike a web server that may face challenges with long-distance data delivery and heavy traffic, a CDN stores content closer to the user, thereby improving speed and reducing bandwidth consumption.
Why Do You Need a CDN?

Employing a CDN can substantially improve your website's performance. It shortens the distance data travels between servers and users, optimizes file sizes, and enhances server efficiency.
CDN Simplified: A Beginner's Guide
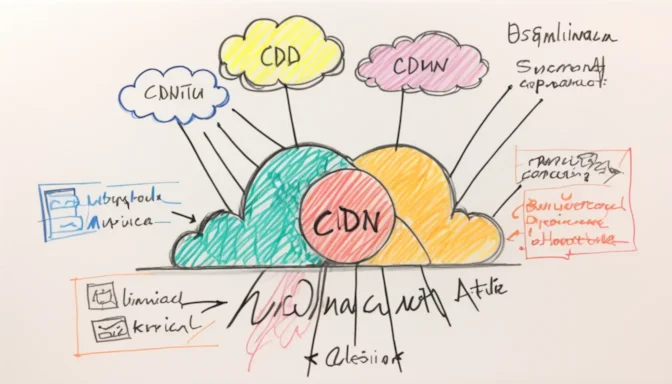
In simple terms, a CDN spreads your website's content closer to where your audience is located. This ensures faster loading times and more reliable access.
CDN in Everyday Language

Consider a CDN as a highway that speeds up the delivery of your website's content by placing it closer to your audience's location.
Is YouTube a CDN?
YouTube employs a CDN to cope with the enormous global demand for video content. This ensures that videos not only load faster but also stream without interruptions.
 E-Commerceo
E-Commerceo